Understanding Vaccines

The science behind vaccines is a fascinating interplay of immunology and public health. Vaccines are biological preparations that provide acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. They work by stimulating the body’s immune response, making it easier to fight off future infections. This article delves into the mechanisms by which vaccines operate and their importance in maintaining public health.
How Vaccines Work

Vaccines contain antigens that resemble a disease-causing microorganism. These antigens are often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. When a vaccine is administered, the immune system recognizes these antigens as foreign and mounts an immune response. This response includes the production of antibodies, which can help neutralize the pathogen if encountered in the future.
The Role of Vaccines in Public Health

Vaccines play a crucial role in public health by preventing outbreaks of contagious diseases. High vaccination coverage within a community leads to herd immunity, which protects those who cannot be vaccinated, such as individuals with certain medical conditions. Vaccines have successfully eradicated diseases like smallpox and significantly reduced the incidence of others, including polio and measles.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of vaccines, misinformation and fear can lead to vaccine hesitancy. Common misconceptions include fears of side effects and the belief that vaccines cause diseases. Public health campaigns aim to address these misconceptions by providing accurate information and promoting the benefits of vaccination.
Conclusion
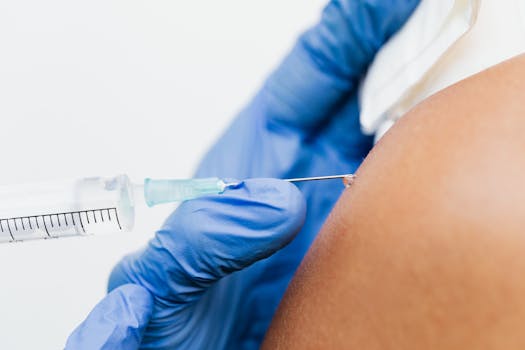
The science behind vaccines is a testament to human ingenuity and our understanding of immunology. Vaccines not only protect individuals but also contribute to the health of communities at large. As we face new health challenges, continued research and public education on vaccines remain critical to safeguarding public health.





