
Understanding Quantum Mechanics and its Implications for Reality
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales. It has been a topic of fascination and research for many decades, and its implications for our understanding of reality are profound. In this article, we will delve into the principles of quantum mechanics and explore its implications for our understanding of the world.
The Principles of Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is based on several key principles, including wave-particle duality, uncertainty, and superposition. Wave-particle duality suggests that particles, such as electrons, can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior depending on how they are observed. The uncertainty principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg, states that certain properties of a particle, such as position and momentum, cannot be precisely known at the same time. Superposition, on the other hand, suggests that particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously, which is a fundamental aspect of quantum computing.
Quantum Mechanics and Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics for our understanding of reality are far-reaching. One of the most significant implications is the concept of non-locality, which suggests that particles can be instantaneously connected regardless of distance. This idea challenges our classical understanding of space and time. Additionally, the concept of superposition and entanglement raises questions about the nature of reality and the role of observation in shaping our understanding of the world.
Experiments and Evidence

There have been numerous experiments and studies that demonstrate the principles of quantum mechanics. The double-slit experiment, for example, shows that particles can exhibit wave-like behavior when unobserved, but particle-like behavior when observed. The EPR paradox, proposed by Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen, highlights the concept of entanglement and non-locality. These experiments and others have consistently shown that quantum mechanics is a fundamental aspect of the natural world.
Implications and Applications
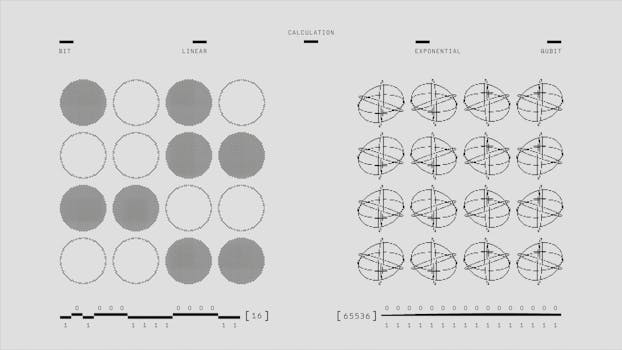
The implications of quantum mechanics are not limited to the realm of physics. Quantum computing, for example, has the potential to revolutionize the way we process information and solve complex problems. Quantum cryptography and secure communication are also being developed, which could have significant implications for data security. Furthermore, the principles of quantum mechanics have inspired new areas of research, such as quantum biology and quantum consciousness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory that has far-reaching implications for our understanding of reality. Its principles, including wave-particle duality, uncertainty, and superposition, have been consistently demonstrated through experiments and studies. The implications of quantum mechanics are not limited to physics, but have the potential to revolutionize various fields, from computing to biology. As we continue to explore and understand the quantum world, we may uncover new and exciting insights into the nature of reality itself.






