
Understanding Quantum Mechanics and its Implications for Reality
Quantum Mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales. Quantum Mechanics has been a topic of fascination for scientists and philosophers alike, as it challenges our classical understanding of reality and raises important questions about the nature of existence.
What is Quantum Mechanics?

Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic level. At these scales, the classical laws of physics no longer apply, and strange, seemingly random phenomena start to occur. Quantum mechanics provides a framework for understanding these phenomena and has been incredibly successful in explaining a wide range of experimental results.
Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics

There are several key principles that underlie quantum mechanics, including:
- Wave-particle duality: The ability of particles, such as electrons, to exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior.
- Uncertainty principle: The idea that certain properties of a particle, such as its position and momentum, cannot be precisely known at the same time.
- Superposition: The ability of a particle to exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- Entanglement: The phenomenon where two or more particles become connected in such a way that their properties are correlated, regardless of the distance between them.
Implications of Quantum Mechanics for Reality

The principles of quantum mechanics have far-reaching implications for our understanding of reality. Some of the most significant implications include:
- The nature of reality is probabilistic: Quantum mechanics suggests that reality is fundamentally probabilistic, rather than deterministic. This means that the outcome of any measurement is uncertain until it is observed.
- The role of observation in shaping reality: The act of observation itself can influence the behavior of particles, which raises questions about the relationship between the observer and the observed.
- The interconnectedness of all things: Entanglement suggests that particles can be connected in a way that transcends space and time, which has led to speculation about the nature of consciousness and the interconnectedness of all things.
Interpretations of Quantum Mechanics
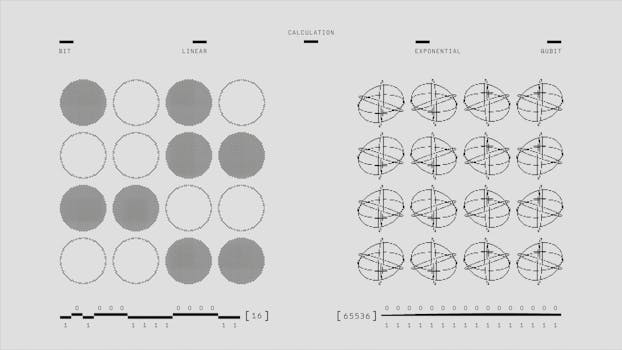
There are several different interpretations of quantum mechanics, each of which attempts to provide a more complete understanding of the theory and its implications. Some of the most popular interpretations include:
- Copenhagen interpretation: This is one of the original interpretations of quantum mechanics, which suggests that the wave function collapses upon measurement.
- Many-worlds interpretation: This interpretation suggests that every possible outcome of a measurement actually occurs in a separate universe.
- Quantum Bayesianism: This interpretation views quantum mechanics as a tool for making probabilistic predictions, rather than a description of an underlying reality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Quantum Mechanics is a powerful and fascinating theory that has far-reaching implications for our understanding of reality. While the principles of quantum mechanics are well established, the interpretation of these principles is still an active area of research and debate. As our understanding of quantum mechanics continues to evolve, we may uncover even more surprising and profound insights into the nature of reality itself.






