Table of Contents
- What is Diabetes?
- Types of Diabetes
- Impact of Diabetes on Daily Life
- Managing Diabetes in Daily Life
- The Importance of Support Systems
What is Diabetes?

Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition that occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: A form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
Impact of Diabetes on Daily Life

1. Dietary Changes
Individuals with diabetes must carefully monitor their carbohydrate intake and overall diet. This often involves:
- Counting carbohydrates to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Choosing whole, unprocessed foods over refined sugars and carbohydrates.
- Planning meals and snacks to maintain stable blood sugar throughout the day.
2. Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for managing diabetes. It helps control weight, lowers blood sugar levels, and reduces the risk of heart disease. Those with diabetes should aim for:
- At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week.
- Incorporating strength training exercises twice a week.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels before and after exercise to avoid hypoglycemia.
3. Emotional and Mental Well-being
Diabetes can also affect mental health. The stress of managing a chronic condition may lead to feelings of anxiety or depression. It’s essential to:
- Recognize and address mental health issues with a healthcare provider.
- Engage in stress-reducing activities like mindfulness and meditation.
- Connect with support groups or counseling services.
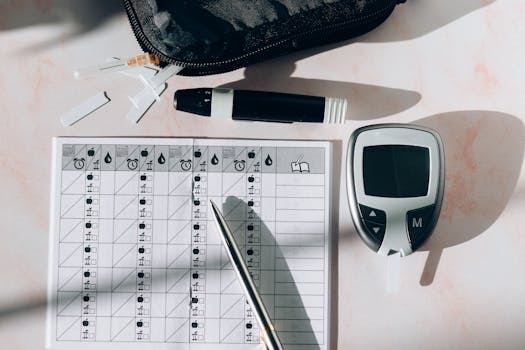
4. Routine Monitoring
Daily monitoring of blood sugar levels is a critical part of diabetes management. This includes:
- Using a glucose meter to check blood sugar levels regularly.
- Keeping track of results to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments.
- Scheduling regular check-ups with healthcare professionals.
Managing Diabetes in Daily Life

1. Education and Awareness
Education about diabetes is vital for effective self-management. This includes understanding:
- The importance of adhering to prescribed medications.
- Recognizing the signs of high and low blood sugar.
- Learning about the impact of food choices and exercise on blood sugar levels.
2. Building Healthy Habits
Establishing healthy habits can significantly improve quality of life. This involves:
- Creating a balanced meal plan that accommodates personal preferences and nutritional needs.
- Setting a consistent exercise routine that fits into your lifestyle.
- Staying hydrated and getting adequate sleep.
3. Utilizing Technology
Technology can aid in managing diabetes effectively. This includes:
- Using apps to track food intake and blood sugar levels.
- Employing continuous glucose monitors for real-time blood sugar tracking.
- Participating in telehealth consultations for convenient access to healthcare services.
The Importance of Support Systems

1. Family and Friends
Having a supportive network can help individuals with diabetes stick to their management plans. Supportive family and friends can:
- Encourage healthy eating and exercise habits.
- Provide emotional support during challenging times.
- Participate in health-related activities together.
2. Healthcare Professionals
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential for optimal diabetes management. They can:
- Provide personalized advice and recommendations.
- Adjust treatment plans as needed based on health changes.
- Offer resources for managing diabetes effectively.
3. Community Resources
Many communities provide resources for individuals with diabetes, such as:
- Support groups that offer shared experiences and coping strategies.
- Classes on nutrition and diabetes management.
- Local events focused on fitness and wellness.
See more:
https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/what-is-diabetes
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/quick-facts.html
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-diabetes




