
Understanding Quantum Mechanics and Its Implications for Reality
Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at an atomic and subatomic level. At these scales, the classical laws of physics do not apply, and strange, seemingly random phenomena govern the behavior of particles. The principles of quantum mechanics were developed in the early 20th century by scientists such as Max Planck, Albert Einstein, and Niels Bohr.
One of the key features of quantum mechanics is wave-particle duality. This concept suggests that particles, such as electrons, can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior depending on how they are observed. This property is difficult to comprehend using classical physics, as it seems to contradict the fundamental principles of reality.
Implications for Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics for our understanding of reality are profound. The theory suggests that, at a fundamental level, reality is made up of probabilities rather than definite outcomes. This means that the act of observation itself can influence the behavior of particles, a concept known as the observer effect.
Furthermore, quantum mechanics introduces the concept of entanglement, where two or more particles become connected in such a way that their properties are correlated, regardless of the distance between them. This phenomenon has been experimentally confirmed and has significant implications for our understanding of space and time.
Quantum Superposition and Entanglement

Quantum superposition is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that suggests that a quantum system can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This property is a direct result of the wave-like behavior of particles and is a key feature of quantum computing and quantum cryptography.
Entanglement, on the other hand, is a phenomenon where two or more particles become connected in such a way that their properties are correlated. This means that if something happens to one particle, it instantly affects the other, regardless of the distance between them. Entanglement has been experimentally confirmed and has significant implications for our understanding of space and time.
Quantum Mechanics and the Nature of Reality
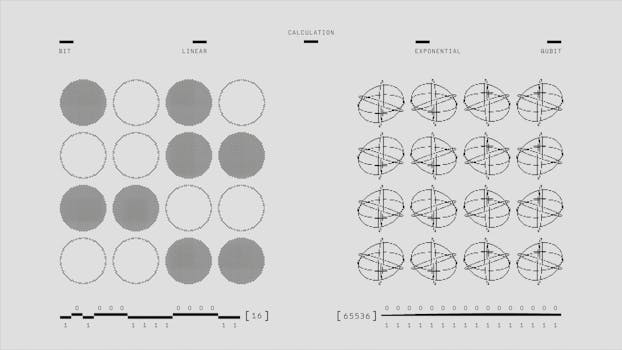
The implications of quantum mechanics for our understanding of reality are still a topic of debate among physicists and philosophers. Some interpretations, such as the Copenhagen interpretation, suggest that the act of observation itself collapses the wave function, effectively creating reality. Others, such as the many-worlds interpretation, suggest that every possible outcome of a quantum event actually occurs in a separate universe.
Regardless of the interpretation, quantum mechanics has significant implications for our understanding of reality. It suggests that, at a fundamental level, reality is made up of probabilities rather than definite outcomes, and that the act of observation itself can influence the behavior of particles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that has far-reaching implications for our understanding of reality. The principles of quantum mechanics, including wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement, have been experimentally confirmed and have significant implications for our understanding of space and time. While the implications of quantum mechanics for our understanding of reality are still a topic of debate, it is clear that this theory has revolutionized our understanding of the world and will continue to shape our understanding of the universe for generations to come.






