
Understanding Quantum Mechanics and Its Implications for Reality
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales. At these scales, the classical laws of physics do not apply, and strange, seemingly random phenomena start to occur. Quantum mechanics is a complex and fascinating field that has led to many important discoveries and innovations, from transistors and lasers to computer chips and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.
Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics
Some of the key principles of quantum mechanics include wave-particle duality, uncertainty principle, and superposition. Wave-particle duality states that particles, such as electrons, can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior. The uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know certain properties of a particle, such as its position and momentum, simultaneously with infinite precision. Superposition states that a particle can exist in multiple states simultaneously, which is known as a quantum superposition.
Implications of Quantum Mechanics for Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics for our understanding of reality are profound. According to the principles of quantum mechanics, the behavior of particles at the subatomic level is fundamentally random and unpredictable. This has led to the concept of the multiverse, which suggests that every possible outcome of every event actually occurs in a separate universe. This idea challenges our understanding of reality and raises questions about the nature of free will and the role of observation in shaping reality.
Quantum Entanglement and Non-Locality
Another important implication of quantum mechanics is the phenomenon of quantum entanglement. When two particles become entangled, their properties become connected in such a way that the state of one particle is instantaneously affected by the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them. This effect has been demonstrated in numerous experiments and has led to a deeper understanding of the nature of reality and the interconnectedness of all things.
Applications of Quantum Mechanics

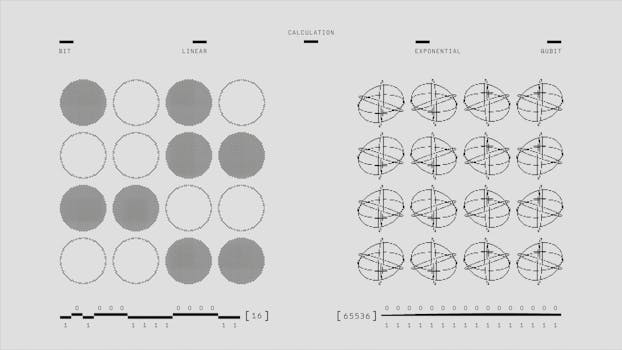
Quantum mechanics has many practical applications in fields such as technology, medicine, and energy. Some examples include quantum computing, which uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations that are exponentially faster than classical computers; quantum cryptography, which uses entangled particles to create secure communication channels; and quantum simulation, which uses quantum systems to simulate complex phenomena and make new discoveries.
Quantum Mechanics and Consciousness
Finally, the study of quantum mechanics has also led to new insights into the nature of consciousness. Some theories, such as the Orchestrated Objective Reduction (Orch-OR) theory, suggest that consciousness arises from quantum mechanical processes in the brain. While these ideas are still highly speculative, they demonstrate the potential for quantum mechanics to shed new light on some of the most fundamental questions about human existence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quantum mechanics is a fascinating and complex field that has led to many important discoveries and innovations. Its implications for our understanding of reality are profound, and its applications in fields such as technology, medicine, and energy are numerous. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the quantum world, we may uncover even more surprising and counterintuitive phenomena that challenge our understanding of the universe and our place within it.






