
What is Quantum Mechanics?

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It serves as a crucial framework for understanding the behavior of matter and energy.
The Core Principles of Quantum Mechanics

At the heart of quantum mechanics are several key principles, including wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement. Wave-particle duality suggests that particles, such as electrons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. Superposition allows quantum systems to exist in multiple states simultaneously until measured, while entanglement describes the phenomenon where particles become interconnected, such that the state of one instantly influences the state of another, regardless of distance.
Implications for Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics extend far beyond theoretical physics. It challenges our classical understanding of reality, suggesting that at a fundamental level, the universe is not deterministic but probabilistic. This raises profound philosophical questions about the nature of reality, consciousness, and the role of the observer in shaping the universe.
Quantum Mechanics and Technology

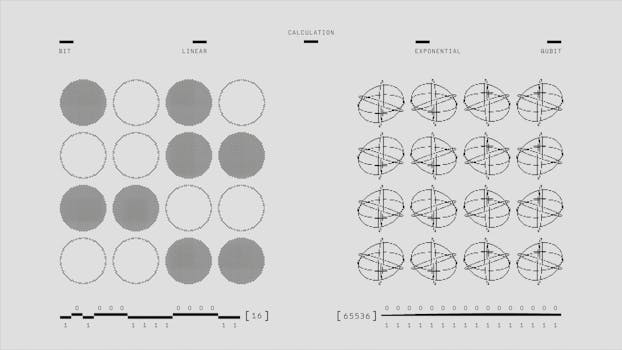
Quantum mechanics also has practical applications that are reshaping technology. Technologies such as quantum computing, quantum cryptography, and MRI scans leverage quantum principles to enhance functionality and efficiency. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize fields ranging from computing to medicine.
Conclusion
Understanding quantum mechanics is crucial for grasping the fabric of reality itself. As we delve deeper into its mysteries, we not only enhance our scientific knowledge but also confront fundamental questions about existence and the universe.






