
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics

Understanding quantum mechanics is essential for grasping the fundamental nature of reality. At its core, quantum mechanics deals with the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales, where classical physics no longer applies. This article delves into the principles of quantum mechanics and explores its implications for our understanding of reality.
The Fundamental Principles of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is based on several key principles. The first is the concept of wave-particle duality, which posits that particles, such as electrons and photons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This duality is famously illustrated by the double-slit experiment, where light behaves as a wave when not observed but acts as particles when measured.
Another principle is the uncertainty principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg, which states that certain pairs of physical properties, like position and momentum, cannot be simultaneously known to arbitrary precision. This principle challenges the deterministic view of classical physics and introduces inherent unpredictability into the behavior of quantum systems.
Quantum Entanglement and Its Mysteries

Quantum entanglement is another intriguing phenomenon that arises in quantum mechanics. When two particles become entangled, the state of one particle is directly related to the state of another, regardless of the distance separating them. This phenomenon has led to debates about the nature of reality, as it appears to defy the classical notion of locality.
Entangled particles can instantaneously affect each other when one is measured, a phenomenon that Albert Einstein famously referred to as “spooky action at a distance.” This raises profound questions about the interconnectedness of the universe and challenges our understanding of causality.
Implications for Reality
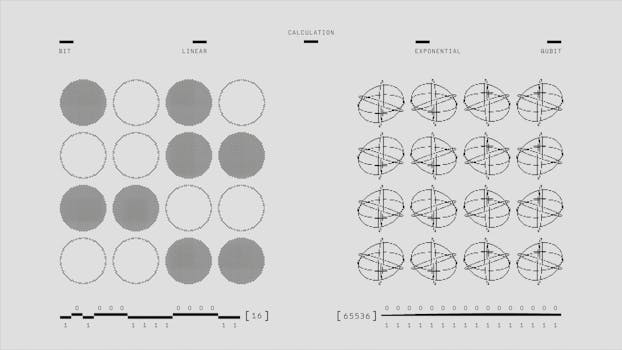
The implications of quantum mechanics for reality are vast and far-reaching. One significant implication is the idea that reality is not as fixed and objective as it appears. The observer effect suggests that the act of observation can alter the state of a quantum system, leading to the conclusion that consciousness may play a role in shaping reality.
Furthermore, the many-worlds interpretation posits that every quantum event creates a branching of the universe into multiple, coexisting realities. This theory raises philosophical questions about the nature of existence and the concept of free will, as each decision leads to the creation of parallel universes.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding quantum mechanics is crucial for grasping the complexities of reality. The principles of wave-particle duality, uncertainty, and entanglement challenge our conventional views and open up new avenues for exploration. As we continue to study these phenomena, we may uncover even deeper insights into the nature of the universe and our place within it.





