
Introduction

Understanding quantum mechanics is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles that govern our universe. This branch of physics challenges traditional notions of reality, offering insights that can seem counterintuitive yet profoundly impactful.
What is Quantum Mechanics?

Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels. Unlike classical physics, which describes the macroscopic world, quantum mechanics introduces concepts such as wave-particle duality and superposition, fundamentally altering our perception of reality.
Key Concepts in Quantum Mechanics

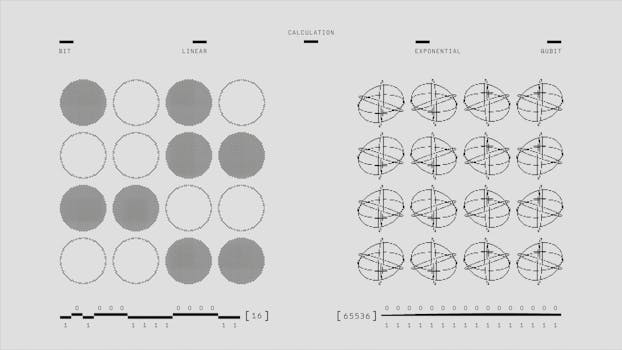
Several key concepts define quantum mechanics:
- Wave-Particle Duality: Particles such as electrons exhibit properties of both waves and particles, depending on how they are observed.
- Superposition: A particle can exist in multiple states simultaneously until it is measured, which collapses the probabilistic wave function into a definite state.
- Entanglement: Particles can become entangled, meaning the state of one particle instantaneously influences the state of another, regardless of distance.
The Implications of Quantum Mechanics for Reality
The implications of quantum mechanics extend beyond physics, impacting philosophy, technology, and our understanding of consciousness. It challenges our concepts of causality and determinism, suggesting a more interconnected and complex reality.
Quantum Mechanics and Technology

Quantum mechanics has led to groundbreaking advancements in technology, including quantum computing and quantum cryptography. These technologies leverage quantum principles to perform computations and secure communications far beyond classical capabilities.
Conclusion

Understanding quantum mechanics is not merely an academic pursuit but a necessary endeavor to grasp the complexities of our reality. As we continue to explore this fascinating field, we unlock new technologies and insights that challenge our perceptions and expand our understanding of existence.






