
What is Quantum Mechanics?

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes nature at the smallest scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles. It challenges our classical understanding of physics by introducing concepts that seem counterintuitive and perplexing.
Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics

One of the core principles of quantum mechanics is wave-particle duality, which posits that particles can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This duality leads to phenomena such as interference and entanglement, where particles become interconnected in ways that classical physics cannot explain.
The Role of Observation
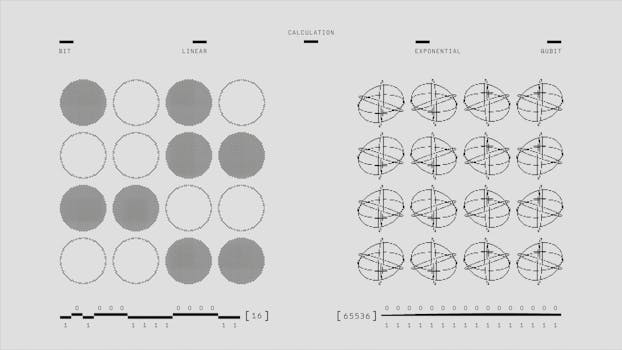
Another intriguing aspect of quantum mechanics is the role of the observer. The act of measurement can influence the state of a quantum system, leading to discussions on the nature of reality itself. This phenomenon raises questions about determinism and free will, suggesting that reality may not be as fixed as we perceive it.
Implications for Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics extend beyond physics into philosophy and metaphysics. It challenges our understanding of reality and suggests that the universe may be interconnected in ways we have yet to fully comprehend. Concepts such as superposition and entanglement invite us to reconsider the nature of existence and the fabric of reality.
Conclusion
Understanding quantum mechanics is essential for grasping the complexities of the universe. Its principles not only advance scientific knowledge but also provoke profound philosophical inquiries about the nature of reality itself. As we continue to explore quantum phenomena, we may uncover deeper truths about the world around us.






