
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics

Understanding quantum mechanics is essential for grasping the fundamental nature of reality. Quantum mechanics describes the behavior of matter and energy on the smallest scales, where classical physics fails to provide accurate predictions. This article will delve into the key concepts of quantum mechanics and their implications for our understanding of reality.
Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is built on several key principles that challenge our classical intuitions. One of the foundational concepts is wave-particle duality, which posits that particles, such as electrons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This duality is famously illustrated by the double-slit experiment, where particles behave differently when observed.
Another crucial principle is superposition, where a quantum system can exist in multiple states simultaneously until it is measured. This leads to the phenomenon of entanglement, where two particles can be linked in such a way that the state of one instantly influences the state of the other, regardless of the distance separating them.
The Role of Observation in Quantum Mechanics

One of the most intriguing aspects of quantum mechanics is the role of the observer. The act of measurement affects the state of a quantum system, leading to what is known as the observer effect. This challenges our traditional understanding of reality as something that exists independently of our observation.
The famous thought experiment known as Schrödinger’s cat illustrates this concept. In this scenario, a cat in a sealed box is simultaneously alive and dead until someone opens the box and observes the cat. This paradox highlights the strange nature of reality at the quantum level, where outcomes are not determined until they are observed.
Implications for Our Understanding of Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics extend beyond physics into philosophy and our understanding of reality. If reality is fundamentally probabilistic rather than deterministic, it raises questions about free will and the nature of existence. Are we mere observers in a universe dictated by quantum probabilities, or do we have agency in shaping our reality?
Moreover, the interconnectedness of quantum particles challenges our notions of separateness and individuality. If everything is entangled, then the boundaries we perceive may be illusory, suggesting a deeper level of unity in the fabric of the universe.
Conclusion
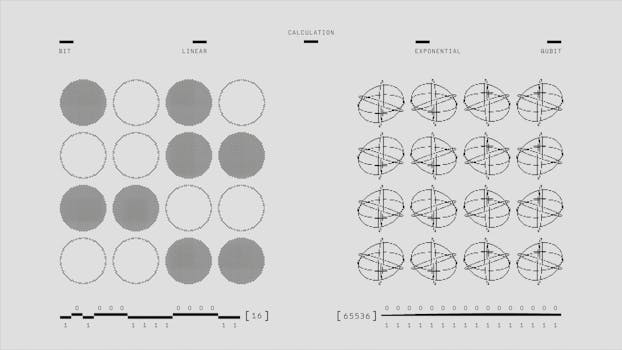
Understanding quantum mechanics opens up a fascinating exploration of the nature of reality. The principles of wave-particle duality, superposition, and the observer effect challenge our classical perceptions and invite us to reconsider our place in the universe. As we continue to explore the quantum realm, we may uncover even deeper truths about the nature of existence and the interconnectedness of all things.






