
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics

Understanding quantum mechanics is essential for unlocking the mysteries of our universe. This field of physics focuses on the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales, particularly at the level of atoms and subatomic particles. The implications of quantum mechanics stretch beyond theoretical physics, affecting our understanding of reality itself.
The Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics

At its core, quantum mechanics challenges classical physics principles. One of the fundamental concepts is the idea of wave-particle duality, which suggests that particles can exhibit properties of both waves and particles. This duality leads to phenomena such as the uncertainty principle, which posits that certain pairs of properties, like position and momentum, cannot both be precisely measured at the same time.
Implications for Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics extend into the philosophical realm, raising questions about the nature of reality. For instance, the phenomenon of entanglement suggests that particles can become connected in ways that transcend classical physics, leading to instantaneous communication between them regardless of distance. This challenges our traditional notions of locality and causality.
Quantum Mechanics and Technology

Beyond its philosophical implications, quantum mechanics has led to significant technological advancements. Quantum computing, for example, harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations much faster than classical computers. This technology has the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, materials science, and artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
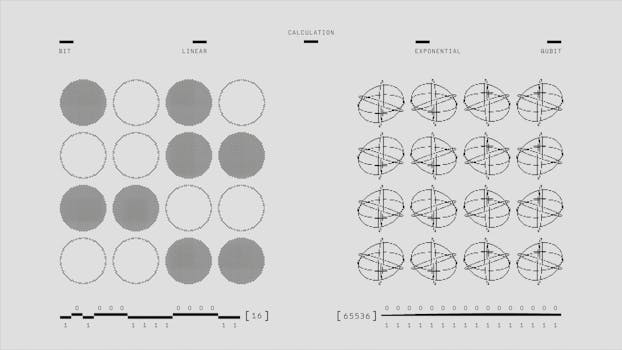
In conclusion, understanding quantum mechanics is not just an academic pursuit; it has profound implications for how we perceive reality and interact with the universe. As we continue to explore the depths of quantum theory, we may unlock even more mysteries that redefine our understanding of existence itself.






