
Understanding Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It challenges our classical notions of reality, introducing concepts that seem counterintuitive.
The Core Principles of Quantum Mechanics
At its core, quantum mechanics revolves around several key principles:
- Wave-Particle Duality: Particles, such as electrons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties.
- Quantum Superposition: Particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously until measured.
- Entanglement: Particles can become correlated in such a way that the state of one instantly influences the state of another, regardless of distance.
Implications for Reality

The implications of quantum mechanics extend far beyond the realm of physics. They force us to reconsider the nature of reality itself:
- Reality as a Construct: The observer effect suggests that the act of observation can alter the outcome of events, leading to questions about whether reality exists independently of our observations.
- Determinism vs. Free Will: Quantum mechanics introduces elements of randomness, challenging traditional deterministic views of the universe.
- Interconnectedness: Quantum entanglement implies a profound interconnectedness between particles, hinting at a more unified view of reality.
Quantum Mechanics in Everyday Life
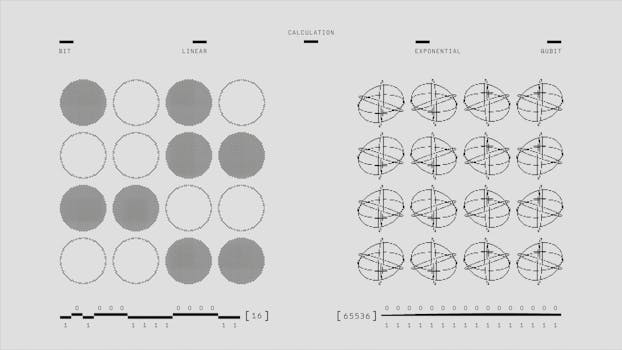
While quantum mechanics may seem abstract, its principles underpin many technologies we use today, such as semiconductors and lasers. Understanding these principles can enhance our appreciation for the technology that shapes our lives.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding quantum mechanics opens up new avenues for exploring the nature of reality. As we delve deeper into this fascinating field, we continue to grapple with its implications, which challenge our perceptions and expand our understanding of the universe.






