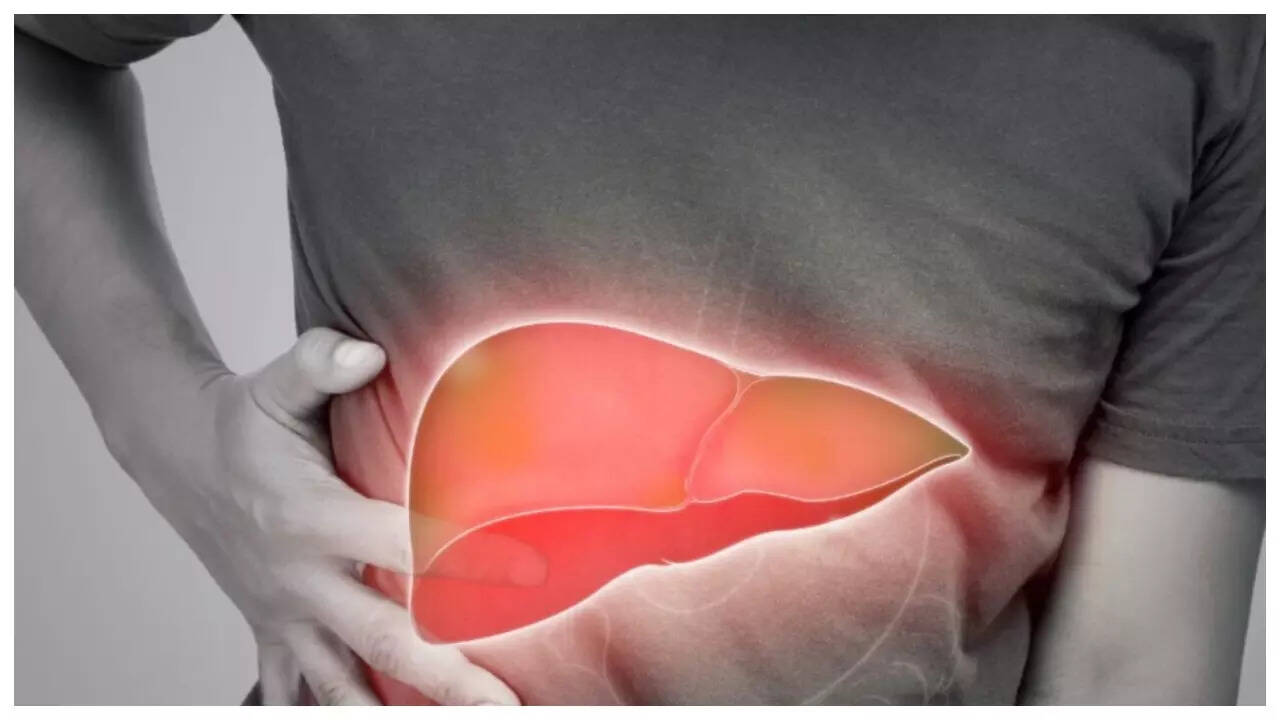
Hepatic steatosis, commonly known as fatty liver disease, occurs when liver tissue accumulates more than 5-10% fat by weight. This condition can stem from excess alcohol intake or weight-related issues like diabetes and poor dietary habits. Sedentary lifestyles are contributing to the rise of fatty liver problems. There are two main grades of fatty liver: Grade 1, a mild stage with minimal damage, and Grade 2, an advanced stage with significant fat accumulation and potential liver cell damage. Early detection and lifestyle adjustments can effectively manage both grades of the disease. By avoiding alcohol, reducing saturated fats, cutting down on processed foods, engaging in regular exercises like walking, and following a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, individuals can help reverse fatty liver conditions.