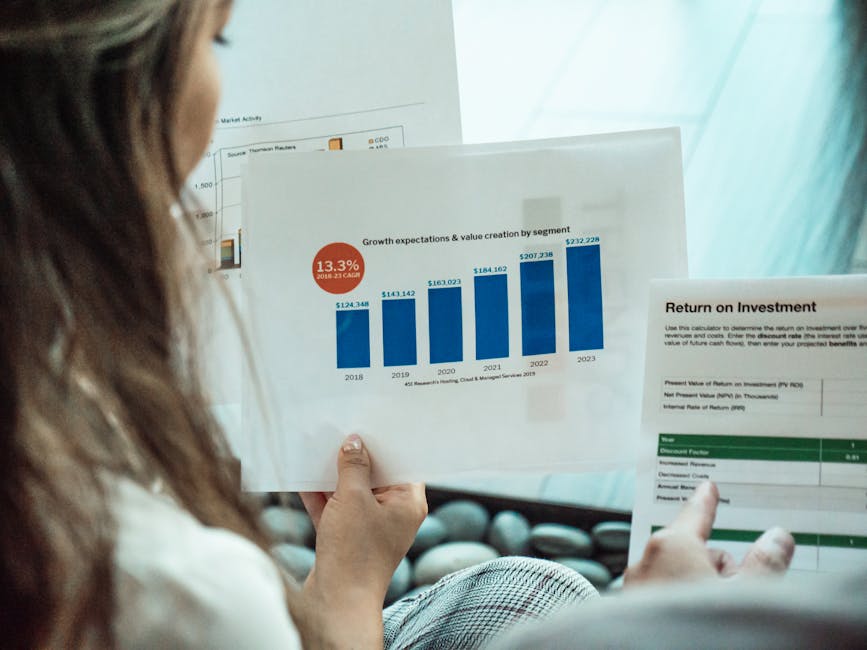
The Science Behind Vaccines and Public Health: Understanding the Importance of Vaccination
The science behind vaccines and public health is a crucial aspect of modern medicine, and vaccines have been instrumental in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and protecting public health. Vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent the spread of diseases, and it has been widely accepted as a vital tool in maintaining public health.
What are Vaccines?

Vaccines are biological preparations that contain a weakened or killed form of a microorganism, such as a virus or bacteria, or a toxin produced by the microorganism. When introduced to the body, the vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies and immune cells that can recognize and fight the specific microorganism, thereby preventing infection.
How Do Vaccines Work?

The science behind vaccines is based on the principle of immunology, which is the study of the immune system and its response to foreign substances. When a vaccine is administered, it introduces a small, harmless piece of a microorganism to the body, which triggers an immune response. The immune system recognizes the microorganism as foreign and produces antibodies and immune cells to fight it. This process is called active immunity, and it provides long-term protection against the specific disease.
Benefits of Vaccination
The benefits of vaccination are numerous, and they include:
- Prevention of Infectious Diseases: Vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, such as measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Protection of Public Health: Vaccination helps to protect public health by preventing the spread of diseases and reducing the risk of outbreaks.
- Reduction of Disease-Related Complications: Vaccination can reduce the risk of disease-related complications, such as pneumonia and meningitis.
Risks and Side Effects of Vaccination

While vaccination is generally safe and effective, there are some risks and side effects associated with it. These include:
- Pain, Redness, and Swelling at the Injection Site: These are common side effects of vaccination and are usually mild and temporary.
- Fever and Headache: Some people may experience fever and headache after vaccination, but these symptoms are usually mild and short-lived.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, people may experience an allergic reaction to a vaccine, which can be severe and life-threatening.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the science behind vaccines and public health is complex and multifaceted. Vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent the spread of infectious diseases and protect public health. While there are some risks and side effects associated with vaccination, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks. By understanding the science behind vaccines and their significance in maintaining public health, we can appreciate the importance of vaccination and take steps to protect ourselves and our communities from the spread of diseases.


