
Understanding Vaccines

The science behind vaccines is rooted in immunology, the study of the immune system. Vaccines are biological preparations that provide acquired immunity to particular infectious diseases. By introducing a harmless component of a pathogen, typically a protein or a weakened form of the pathogen, vaccines stimulate the body’s immune response without causing the disease itself.
The Mechanism of Action

When a vaccine is administered, it triggers the immune system to produce antibodies, which are proteins that recognize and neutralize pathogens. This process mimics the natural infection process, resulting in the formation of memory cells that remain in the body long after the vaccination. These cells enable the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively if exposed to the actual pathogen in the future.
Vaccination and Herd Immunity

Vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to herd immunity. Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a population becomes immune to a disease, making its spread unlikely. This concept is crucial in protecting those who cannot be vaccinated, such as individuals with certain medical conditions or allergies.
The Role of Vaccines in Public Health
Vaccines have played a transformative role in public health by drastically reducing the incidence of infectious diseases such as polio, measles, and smallpox. Through widespread vaccination campaigns, these diseases have been eradicated or significantly diminished in many parts of the world, leading to increased life expectancy and improved quality of life.
Challenges and Misconceptions
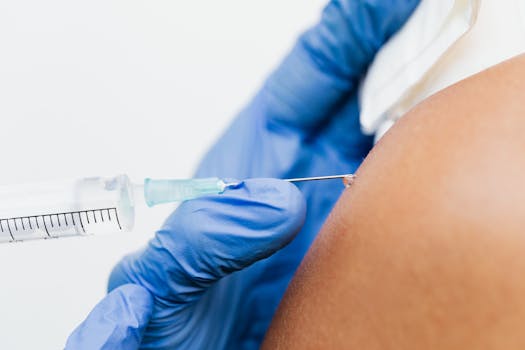
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of vaccines, misconceptions persist. Misinformation can lead to vaccine hesitancy, which poses a threat to public health. It is vital to address these misconceptions by providing accurate information and fostering community trust in vaccination programs.
Conclusion

The science behind vaccines is a testament to human ingenuity and the power of modern medicine. By understanding how vaccines work and their role in public health, we can appreciate the importance of immunization in safeguarding our communities. Vaccination remains one of the most effective tools in preventing infectious diseases and ensuring a healthier future for all.





