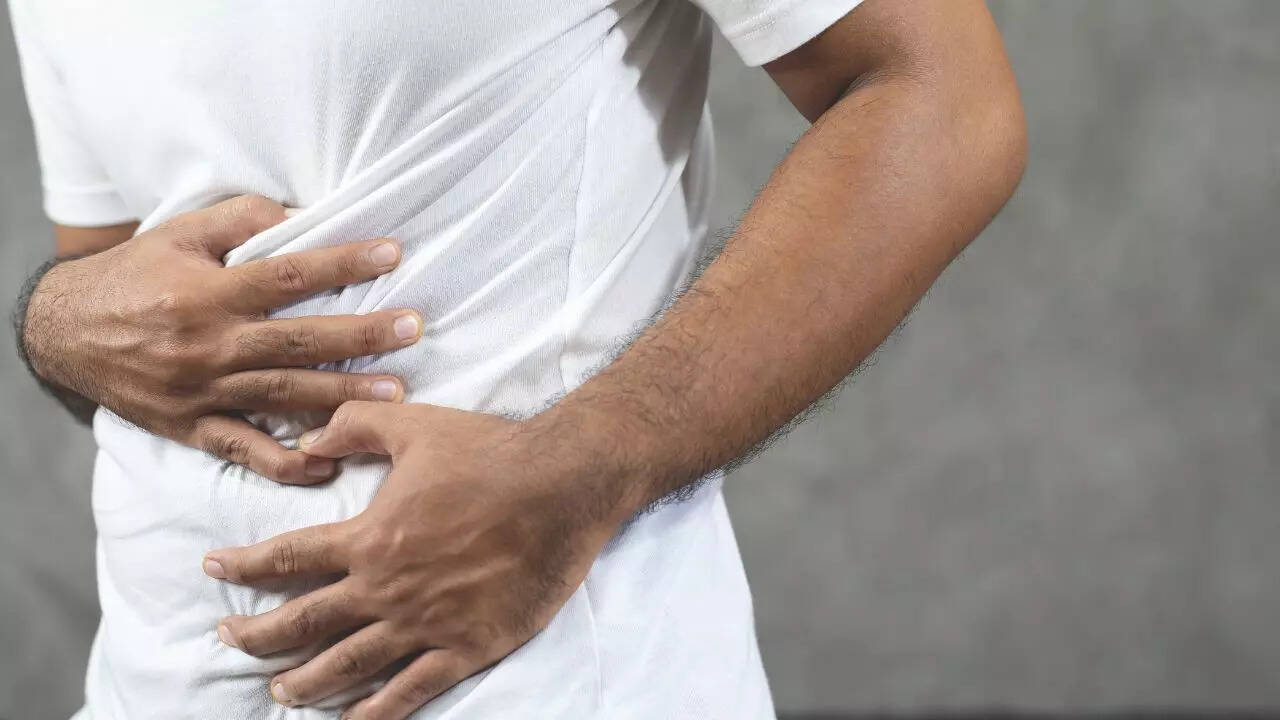
Frequent consumption of oily food poses significant health risks, including digestive discomfort and increased susceptibility to foodborne illnesses. These risks extend to severe conditions like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, weight gain, liver disease, and skin problems. Limiting greasy foods is crucial for mitigating long-term health consequences. Many oily foods high in trans and saturated fats are linked to digestive issues, unwanted weight gain, high cholesterol levels, heart disease, diabetes, and liver conditions. Understanding the harmful effects of these foods is essential for making better dietary choices. By reducing greasy food intake and opting for healthier cooking methods, individuals can safeguard themselves against potential long-term health risks.