Introduction to Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It introduces concepts that challenge our classical understanding of reality, including wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle.
Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics

At its core, quantum mechanics reveals that particles can exist in multiple states at once, a concept known as superposition. When observed, these particles ‘collapse’ into a single state, leading to the famous thought experiment known as Schrödinger’s cat, which exemplifies this principle.
The Uncertainty Principle

One of the most significant implications of quantum mechanics is the uncertainty principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg. This principle states that certain pairs of physical properties, like position and momentum, cannot both be known to arbitrary precision. This intrinsic uncertainty challenges our deterministic view of the universe.
Quantum Entanglement and Reality
Quantum entanglement is another fascinating aspect of quantum mechanics, where two particles become interconnected, such that the state of one particle instantly influences the state of the other, regardless of the distance separating them. This phenomenon raises questions about the nature of reality and the limits of communication and information transfer.
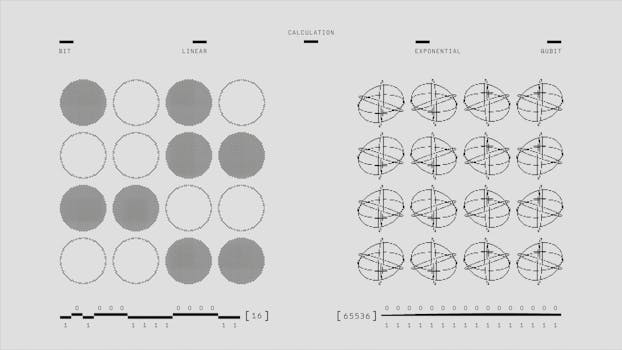
Implications for Technology and Philosophy
The implications of quantum mechanics extend beyond physics into technology and philosophy. Quantum computing, for instance, leverages the principles of superposition and entanglement to perform calculations at unprecedented speeds. Philosophically, quantum mechanics invites us to reconsider the nature of reality, existence, and our perception of the universe.
Conclusion

Understanding quantum mechanics reshapes our comprehension of reality. It reveals a universe that is more complex, interconnected, and uncertain than previously thought. As we continue to explore these concepts, we must remain open to the profound implications they hold for science, technology, and philosophy.




