
Introduction

Understanding quantum mechanics is essential for grasping the fundamental nature of reality. Quantum mechanics, the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales, challenges our classical perceptions of the universe. This article will explore the key principles of quantum mechanics and their implications for reality.
What is Quantum Mechanics?

Quantum mechanics emerged in the early 20th century as scientists sought to explain phenomena that classical physics could not. It describes the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels, where the rules of classical physics break down. The core principles of quantum mechanics include wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement.
Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics

Wave-Particle Duality
One of the most intriguing aspects of quantum mechanics is wave-particle duality. It suggests that particles, such as electrons and photons, can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. For instance, light can behave as a wave, demonstrating interference patterns, yet can also be detected as discrete particles known as photons.
Superposition
Superposition is another fundamental principle of quantum mechanics. It states that a quantum system can exist in multiple states simultaneously until it is observed or measured. This phenomenon is famously illustrated by Schrödinger’s cat thought experiment, where a cat in a box can be considered simultaneously alive and dead until someone opens the box to check.
Entanglement
Entanglement refers to the phenomenon where two or more particles become interconnected in such a way that the state of one particle instantly influences the state of the other, regardless of the distance separating them. This strange connection challenges classical intuitions about locality and causality.
Implications for Reality
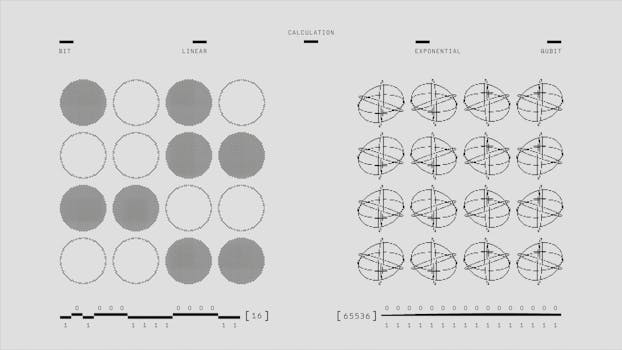
The implications of quantum mechanics extend far beyond the realm of physics. They provoke philosophical questions about the nature of reality itself. If particles can exist in multiple states and influence each other instantaneously, what does that mean for our understanding of causality and determinism?
The Observer Effect
The observer effect suggests that the act of observation affects the state of a quantum system. This raises questions about the role of consciousness in shaping reality. Are we mere observers, or do we actively participate in the unfolding of the universe?
Quantum Reality vs. Classical Reality
In classical physics, reality is deterministic; everything follows predictable laws. However, quantum mechanics introduces an element of randomness and uncertainty. This dichotomy leads to interpretations of reality that challenge our intuitive understanding, suggesting that at a fundamental level, reality may not be as solid and fixed as we perceive it.
Conclusion
Understanding quantum mechanics is key to unlocking the mysteries of reality. Its principles challenge our classical notions and provoke profound philosophical questions. As we continue to explore the quantum realm, we may find that the universe is far more complex and interconnected than we ever imagined.






