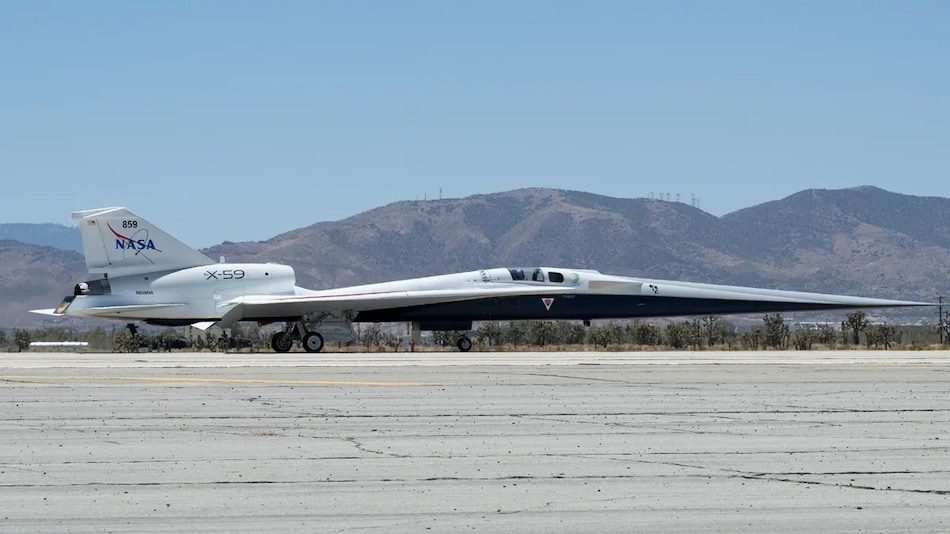
The X-59 aircraft from NASA is designed to fly faster than the speed of sound without causing sonic booms typical of supersonic flights. This 99-foot aircraft has a unique elongated design, removing the front windscreen for a futuristic look. Pilots can now view the front using an augmented reality (AR) closed-circuit camera system called the External Vision System (XVS).
X-59’s Futuristic Design: Eliminating Sonic Booms with External Vision System
During the taxi tests, test pilot Nils Larson slowly navigated the X-59 on the runway to check the steering and braking systems. Lockheed Martin and NASA will conduct high-speed taxi tests to prepare for takeoff.
Taxi Tests at Plant 42: NASA and Lockheed Martin Prepare X-59 for First Flight
The taxi tests are taking place at the U.S. Air Force’s Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, a facility used for aircraft manufacturing and testing. Lockheed Martin, located in Plant 42, developed the X-59.
Several advanced U.S. military aircraft, including the B-2 Spirit, F-22 Raptor, and the RQ-170 Sentinel spy drone, have been partially developed at Plant 42. The SOFIA airborne observatory aircraft, nicknamed the flying telescope, recently retired from Plant 42.
Taxi tests have been ongoing, with collaborations between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency to test a scale model of the X-59 in a supersonic wind tunnel to study the noise produced by the aircraft.